고려대학교는 김영근 공과대학 신소재공학부 교수 연구팀이 차세대 반도체 금속배선로 주목받고 있는 루테늄(Ru)을 나노크기로 제작하고, 지름별로 비저항과 물질 확산 여부를 확인했다고 12일밝혔다. 연구 결과는 지난달 13일 금속학 분야 최상위 국제학술지인 저널 오브 머티리얼즈 사이언스 & 테크놀로지(Journal of Materials Science & Technology) 온라인 게재됐다.
반도체 주요 공정 중 하나인 금속배선(metallization)은 마치 빌딩을 연결하는 도로망처럼, 실리콘 웨이퍼 상에 형성된 반도체 소자들을 연결하는 공정이다. 손톱만한 반도체 칩 한 개에는 수십 km 길이의 구리(Cu) 배선이 사용되며, 전자가 흐르는 통로로 정보를 전달하는 역할을 한다. 최근 반도체 칩의 계속된 집적화로 인해 배선의 선폭이 수 나노미터(nm)까지 줄어들었고, 이 과정에서 배선의 저항이 급격히 증가하는 문제에 직면해 있다.
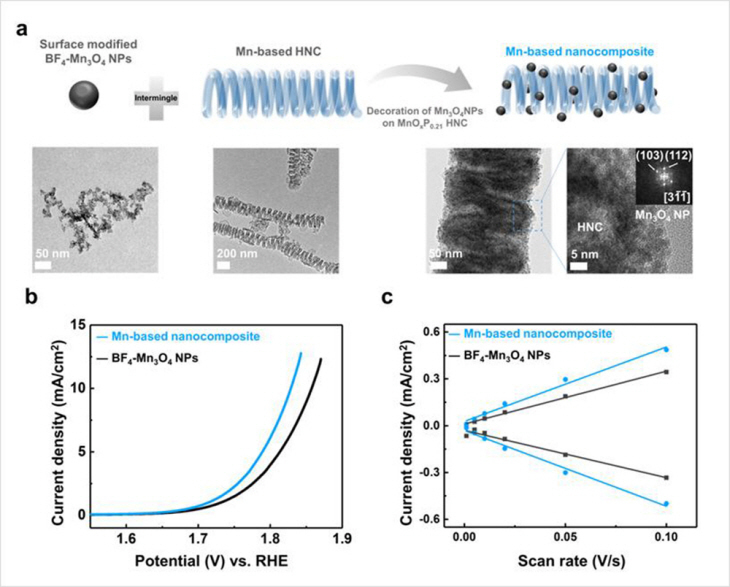
연구팀은 다공성 나노 멤브레인과 전기도금법을 이용하여 루테늄(Ru, 원자번호 44)계 나노선을 제작했다. 루테늄은 비저항 크기 효과가 작고 원자간 응집력도 높아 전기 이동(electromigration)과 배선 주변을 감싸고 있는 유전체 막으로 확산되는 경향이 낮아 차세대 배선 소재 중 하나로 주목받고 있다.
다만, 수용액에서 전기도금 시 경쟁반응인 수소 발생 반응으로 인해 금속 루테늄으로 환원하기가 어려운 문제점이 있었다. 그러나 연구팀은 도금액에 수소 발생을 억제할 수 있는 완충제와 첨가제를 사용하여 다양한 지름을 갖는 루테늄계 나노선을 제작할 수 있었다. 진공 상태의 정교한 측정장비를 이용하여 루테늄 나노선 한 가닥의 저항을 측정했고, 전자산란 계수를 도출했다.
다공성 멤브레인 벽 내부를 저유전체 산화실리콘(SiO2) 막으로 코팅하고 루테늄을 채운 후, 반도체의 후공정 온도에서 열처리했다. 원소분석 결과 루테늄이 산화실리콘 쪽으로 확산되지 않았다. 이번 연구 성과는 삼성미래기술육성사업의 지원을 받아 진행됐고, 이후 착수된 삼성전자 반도체연구소 산학과제의 지원을 받아 추가 연구가 진행됐다.

출처: 매일일보, 2021.10.12, http://www.m-i.kr/news/articleView.html?idxno=866084
Electrical resistivity evolution in electrodeposited Ru and Ru-Co nanowires
Journal of Materials Science & Technology 105, 17-25. (2022)
[DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2021.06.073]
Nanoscale ruthenium (Ru)-based materials are promising replacements for existing multilayered Cu interconnects in integrated circuits. However, it is not easy to apply the results of previously reported studies directly to the electrochemical damascene process because the previous studies have mainly focused on thin films by dry deposition. Here, we report the electrical resistivity and microstructure of electrodeposited Ru nanowires. We estimate that the resistivity value of a 10 nm diameter Ru nanowire to be 71.6 μΩ cm after analyzing the resistivity values of individual nanowires with various diameters. Furthermore, we investigate the electrical properties of RuxCo1-x nanowires where x is 0.04–0.99 at.% as possible replacements of the current TaN barrier structures. Over the entire composition range, the resistivity values of alloys are much lower than that of the conventional TaN. Additionally, Ru and Ru-alloy nanowires surrounded by dielectric silica are thermally stable after 450 °C heat treatment. Therefore, the nanoscale Ru and Ru-Co alloys possessing low resistivity values can be candidates for the interconnect and barrier materials, respectively.